Instagram is redesigning its teen interface with the goal of giving parents more control and assurance, as well as more "built-in protections" for their children.
Tuesday marks the launch of the new "teen accounts" in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
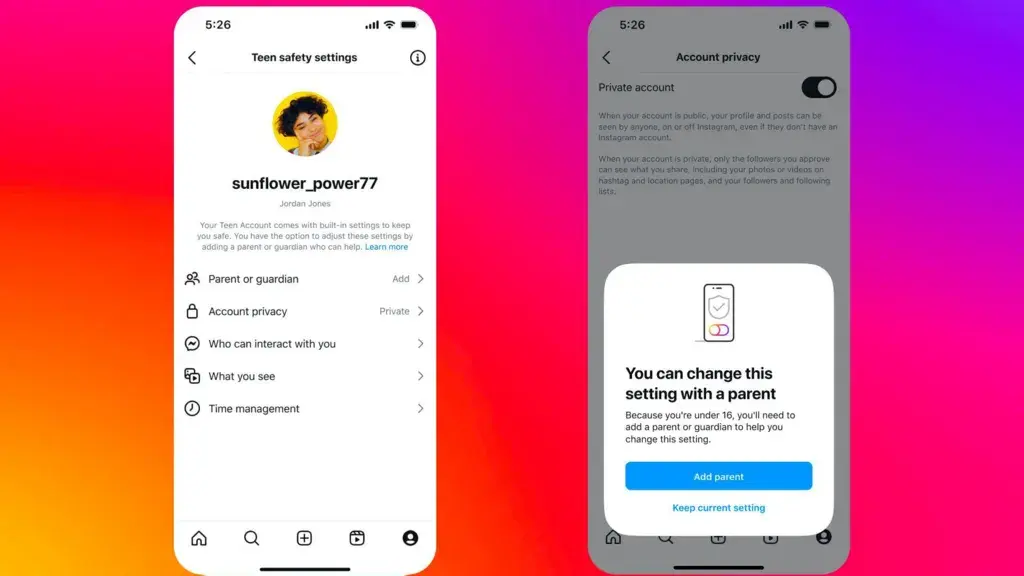
They will turn many privacy settings on by default for all under 18s, including making their content unviewable to people who don't follow them, and making them actively approve all new followers.
But children aged 13 to 15 will only be able to adjust the settings by adding a parent or guardian to their account.
Social media companies are under pressure worldwide to make their platforms safer, with concerns that not enough is being done to shield young people from harmful content.
UK children's charity the NSPCC said Instagram’s announcement was a "step in the right direction".
But it added that account settings can “put the emphasis on children and parents needing to keep themselves safe."
Rani Govender, the NSPCC’s online child safety policy manager, said they "must be backed up by proactive measures that prevent harmful content and sexual abuse from proliferating Instagram in the first place”.
Meta describes the changes as a "new experience for teens, guided by parents".
It says they will "better support parents, and give them peace of mind that their teens are safe with the right protections in place."
Ian Russell, whose daughter Molly viewed content about self-harm and suicide on Instagram before taking her life aged 14, told the BBC it was important to wait and see how the new policy was implemented.
“Whether it works or not we’ll only find out when the measures come into place," he said.
“Meta is very good at drumming up PR and making these big announcements, but what they also have to be good at is being transparent and sharing how well their measures are working."
How will it work?
Teen accounts will mostly change the way Instagram works for users between the ages of 13 and 15, with a number of settings turned on by default.
These include strict controls on sensitive content to prevent recommendations of potentially harmful material, and muted notifications overnight.
Accounts will also be set to private rather than public - meaning teenagers will have to actively accept new followers and their content cannot be viewed by people who don't follow them.
Parents who choose to supervise their child's account will be able to see who they message and the topics they have said they are interested in - though they will not be able to view the content of messages.
However, media regulator Ofcom raised concerns in April over parents' willingness to intervene to keep their children safe online.
In a talk last week, senior Meta executive Sir Nick Clegg said: “One of the things we do find… is that even when we build these controls, parents don’t use them.”
Age identification
The system will primarily rely on users being honest about their ages, but Instagram already uses tools to verify a user's age if they are suspected to be lying about their age.
From January, in the US, it will use artificial intelligence (AI) tools to proactively detect teens using adult accounts, to put them back into a teen account.
The UK's Online Safety Act, passed earlier this year, requires online platforms to take action to keep children safe, or face huge fines.
Ofcom warned social media sites in May they could be named, shamed or banned for under-18s if they fail to comply with its new rules.
Social media industry analyst Matt Navarra said Instagram's changes were significant, but hinged on enforcement.
"As we've seen with teens throughout history, in these sorts of scenarios, they will find a way around the blocks, if they can," he told the BBC.
Questions for Meta
Instagram is not the first platform to introduce such tools for parents - and already claims to have more than 50 tools aimed at keeping teens safe.
In 2022 it introduced a family centre and supervision tools for parents, letting them see accounts their child follows and who follows them, among other features.
Snapchat also introduced its own family centre allowing parents over the age of 25 see who their child is messaging and limit their ability to view certain content.
YouTube said in September it would limit recommendations of certain health and fitness videos to teenagers, such as those which "idealise" certain body types.
Instagram's new measures raises the question of why, despite the large number of protections on the platform, young people are still exposed to harmful content.
An Ofcom study earlier this year found that every single child it spoke to had seen violent material online, with Instagram, WhatsApp and Snapchat being the most frequently named services they found it on.
Under the Online Safety Act, platforms will have to show they are committed to removing illegal content, including child sexual abuse material (CSAM) or content that promotes suicide or self-harm.
But the rules are not expected to fully take effect until 2025.
In Australia, Prime Minister Anthony Albanese recently announced plans to ban social media for children by bringing in a new age limit for kids to use platforms.
Instagram’s latest tools put more control in the hands of parents, who will now take even more direct responsibility for deciding whether to allow their child greater freedom on Instagram, and supervising their activity and interactions.
They will also need to have their own Instagram account.
But parents cannot control the algorithms which push content towards their children, or what is shared by its billions of users around the world.
Social media expert Paolo Pescatore said it was an "important step in safeguarding children’s access to the world of social media and fake news."
"The smartphone has opened up to a world of disinformation, inappropriate content fuelling a change in behaviour among children," he said.
"More needs to be done to improve children’s digital wellbeing and it starts by giving control back to parents."







.svg)
